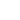The SIGLENT SDG2000X and SDG6000X feature 16-bit voltage step resolution. This provides 65,535 discrete voltage steps that can cover the entire output range (20 Vpp into a High Z load) which can effectively be used to test A/D converters and other measurement systems by sourcing waveforms with very small changes.
In this example, we use Python 2.7 and PyVISA 1.8 to create a ramp waveform that is comprised of steps of the Least Significant Bit (LSB) from point 0 to 65535 on Channel 1.
We also implement the TrueArb function that allows you to specify the sample rate and also ensures that each sample is sourced.
NOTE: You will need to change the instrument ID to match your specific instrument. We also recommend setting the amplitude and other instrument parameters prior to enaling the output of the instrument.
Here is pic of the instrument after loading the waveform:
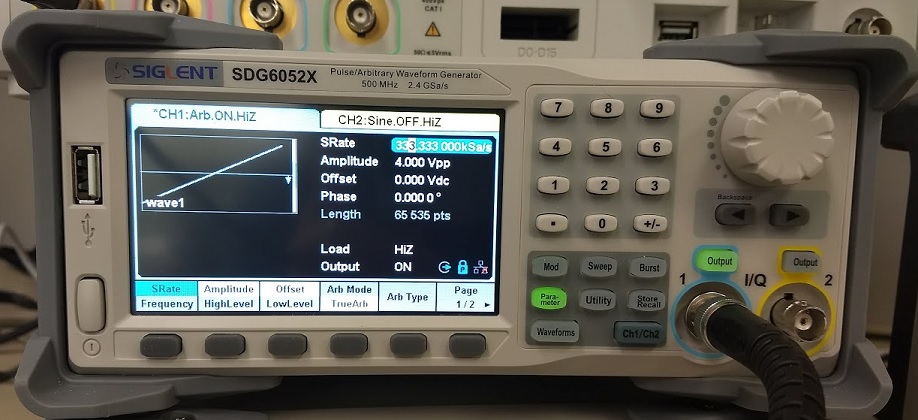
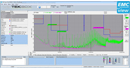
Here is a scope shot of the output:
Here is a link to a Zipped version of the .PY file: SiglentSDG16BBitSteps
Here is the text of the program:
##
#!/usr/bin/env python2.7
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import visa #Uses PyVISA 1.8 and NI-VISA runtime Engine 15.5
import time
import binascii
#USB resource of Device
rm = visa.ResourceManager()
device = rm.open_resource(‘USB0::0xF4EC::0x1101::SDG6XBAQ1R0071::INSTR’) #CHANGE TO MATCH YOUR INSTRUMENT ID
#Little endian, 16-bit 2’s complement
# create a waveform
wave_points = []
for pt in range(0x8000, 0xffff, 1):
wave_points.append(pt)
wave_points.append(0xffff)
for pt in range(0x0000, 0x7fff, 1):
wave_points.append(pt)
def create_wave_file():
#create a file
f = open(“wave1.bin”, “wb”)
for a in wave_points:
b = hex(a)
#print ‘wave_points: ‘,a,b
b = b[2:]
len_b = len(b)
if (0 == len_b):
b = ‘0000’
elif (1 == len_b):
b = ‘000’ + b
elif (2 == len_b):
b = ’00’ + b
elif (3 == len_b):
b = ‘0’ + b
b = b[2:4] + b[:2] #change big-endian to little-endian
c = binascii.a2b_hex(b) #Hexadecimal integer to ASCii encoded string
f.write(c)
f.close()
def send_wave_data(dev):
#send wave1.bin to the device
f = open(“wave1.bin”, “rb”) #wave1.bin is the waveform to be sent
data = f.read()
print (“write bytes:”,len(data))
dev.write_raw(“C1:WVDT WVNM,wave1,FREQ,2000.0,TYPE,8,AMPL,4.0,OFST,0.0,PHASE,0.0,WAVEDATA,%s” % (data))
#”X” series (SDG1000X/SDG2000X/SDG6000X/X-E)
dev.write(“C1:ARWV NAME,wave1”)
f.close()
if __name__ == ‘__main__’:
create_wave_file()
send_wave_data(device)
device.write(“C1:SRATE MODE,TARB,VALUE,333333,INTER,LINE”) #Use TrueArb and fixed sample rate to play every point
###






























































































 FREE SHIPPING £75+
FREE SHIPPING £75+
 CELEBRATING 50+ YEARS
CELEBRATING 50+ YEARS
 PRICE MATCH GUARANTEE
PRICE MATCH GUARANTEE