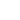
How to Extract FFT Data from the Rigol DHO914S Using Python
If you’re using the Rigol DHO914S oscilloscope and want to perform FFT analysis beyond the scope’s built-in display, you’re in luck. This guide will show you how to:
✅ Export waveform data from the DHO914S
✅ Apply a Hanning window
✅ Compute and plot the FFT magnitude spectrum
✅ Add interactive or automatic peak markers
✅ Optionally export the results to CSV
🧾 Step 1: Export the CSV File from the Oscilloscope
On your Rigol DHO914S:
- Capture a waveform on Channel 1 (CH1).
- Press
Storage>File Type> Select CSV. - Save the data to a USB stick or via network.
- Transfer it to your PC.
You’ll get a .csv file that looks like this:
python-replCopyEditCH1V, t0 =-1.000000e-02, tInc = 2.000000e-06
-0.786533,,,
0.386800,,,
...
Step 2: Load and Process the Data in Python
Install required libraries if you haven’t already:
bashCopyEditpip install numpy pandas matplotlib scipy
Now use the following script:
pythonCopyEditimport numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import find_peaks
# --- Load CSV from Rigol DHO914S ---
filename = "RigolDS0.csv" # Replace with your filename
df = pd.read_csv(filename)
voltage = df['CH1V'].dropna().to_numpy()
N = len(voltage)
# --- Sampling Information (from file header) ---
t_inc = 2e-6 # 2 µs time interval
fs = 1 / t_inc # 500 kHz sample rate
# --- Apply Hanning Window ---
window = np.hanning(N)
windowed_signal = voltage * window
# --- Perform FFT ---
X = np.fft.fft(windowed_signal)
freqs = np.fft.fftfreq(N, d=t_inc)
half_N = N // 2
freqs = freqs[:half_N]
magnitude = (2 / N) * np.abs(X[:half_N]) # Normalized magnitude
# --- Automatically Detect Peaks ---
peak_indices, _ = find_peaks(magnitude, height=0.1) # Adjust threshold
peak_freqs = freqs[peak_indices]
peak_amps = magnitude[peak_indices]
# --- Plot FFT Spectrum with Peaks ---
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.plot(freqs, magnitude, label="FFT Magnitude")
plt.plot(peak_freqs, peak_amps, 'ro', label="Detected Peaks")
for f, a in zip(peak_freqs, peak_amps):
plt.annotate(f"{f:.1f} Hz", xy=(f, a), xytext=(f, a + 0.05),
ha='center', fontsize=8)
plt.title("FFT Spectrum with Peak Detection (Hanning Window)")
plt.xlabel("Frequency (Hz)")
plt.ylabel("Amplitude")
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# --- Print Peak Info ---
print("Detected Peaks:")
for i in range(len(peak_freqs)):
print(f"Peak {i+1}: Frequency = {peak_freqs[i]:.2f} Hz, Amplitude = {peak_amps[i]:.4f}")
Optional: Click to Manually Mark Peaks
If you’d rather click directly on the FFT plot to inspect peaks manually:
pythonCopyEditplt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.plot(freqs, magnitude)
plt.title("Click to Mark Peaks (Press Enter When Done)")
plt.xlabel("Frequency (Hz)")
plt.ylabel("Amplitude")
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show(block=False)
print("Click on peaks to mark them (press Enter when done)...")
clicks = plt.ginput(n=-1, timeout=0)
for i, (fx, _) in enumerate(clicks):
idx = np.argmin(np.abs(freqs - fx))
print(f"Marker {i+1}: Frequency = {freqs[idx]:.2f} Hz, Amplitude = {magnitude[idx]:.4f}")
Optional: Save FFT Spectrum to CSV
You can export the FFT data for use in Excel or other tools:
pythonCopyEditfft_df = pd.DataFrame({
'Frequency (Hz)': freqs,
'Amplitude': magnitude
})
fft_df.to_csv("fft_output.csv", index=False)
Summary
Using Python, you can go far beyond what the Rigol DHO914S shows on screen:
- Perform FFT on high-resolution waveforms
- Apply windowing functions like Hanning
- Detect or interactively mark signal peaks
- Export the data for further analysis or reporting































































































 FREE SHIPPING £75+
FREE SHIPPING £75+
 CELEBRATING 50+ YEARS
CELEBRATING 50+ YEARS
 PRICE MATCH GUARANTEE
PRICE MATCH GUARANTEE