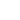CC-CV Charging System without Series Diode
To charge batteries, it is recommended that you connect a diode in series at an output of DC power supply (See Figure 1). With a diode, constant current (CC) can be properly supplied; however constant voltage (CV) may be unstable if using remote sensing at battery terminals. Without a diode, a high current can flow between a battery and power supply when connecting or disconnecting a battery. Now, let me tell you other stable CC-CV charging methods with a switch instead of a diode.
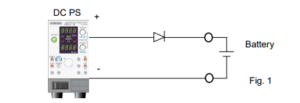
1. Connect Sense Leads to Battery
1.1 System Structure
Connect a double switch (SW1) as shown in Figure 2; one is for the output on/off switch and the other is for the sensing (+S) on/off switch.
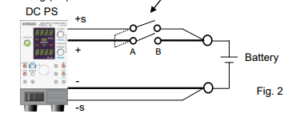
1.2 How to Set Voltage and Turn SW1 On
Set the output voltage equal to the battery voltage and then turn SW1 on.
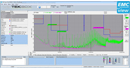
Figure 3 shows the output voltage, output current and voltage at both terminals (A/B) of SW1 when SW1 is turned on.
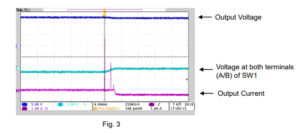
First, the output voltage increases by approx. 0.6 V because the sensing switch (+S) is open. At the time when SW1 is turned on, the small overcurrent is generated because an output current starts flowing or a switch chattering occurs. After SW1 is turned on, the output voltage becomes nearly equal to the battery voltage; the current will stop flowing.
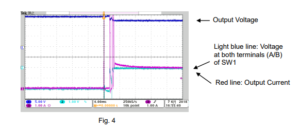
Finally, apply CV voltage to start CC-CV charging.
Note: If you initially set CV voltage and then turn SW1 on, an excess overcurrent flows as shown in Figure 4.
2. Connect Sense Leads to Switch
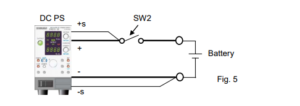
Figure 5 shows how to connect sense leads to switch (SW2). Set the output voltage equal to the battery voltage and turn SW2 on; an overcurrent will not flow.
Then, apply CV voltage to start CC-CV charging.
3. Others
Above systems can serve as your reference. Before configuring your own system, please be sure what type of switch you need.































































































 FREE SHIPPING £75+
FREE SHIPPING £75+
 CELEBRATING 50+ YEARS
CELEBRATING 50+ YEARS
 PRICE MATCH GUARANTEE
PRICE MATCH GUARANTEE